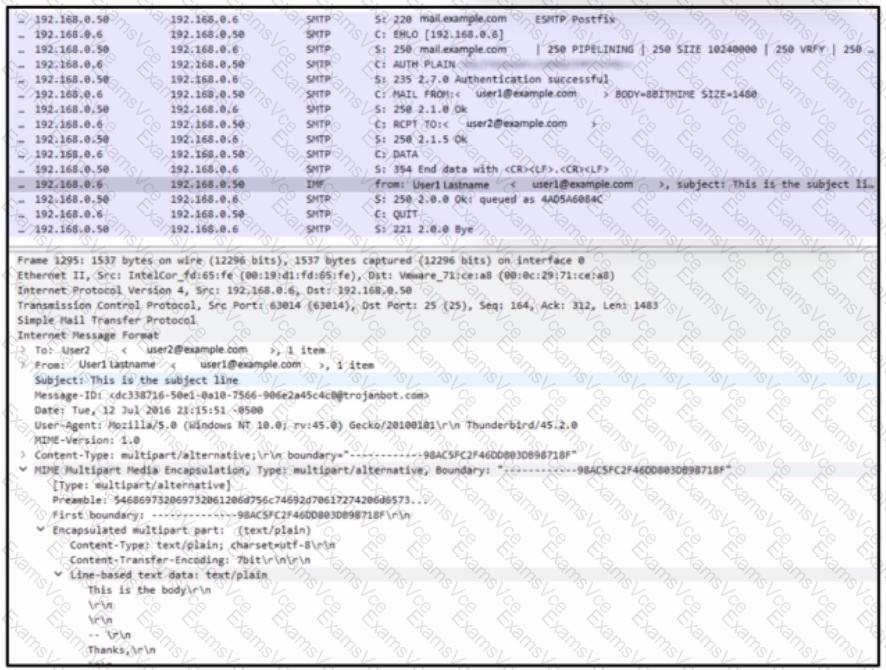
The exhibit indicates that email traffic is being transmitted in clear text, meaning the contents of the communication are readable without encryption. In network intrusion analysis, this is commonly observed when Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) traffic is captured on standard ports such as 25 or 587 without Transport Layer Security (TLS) enabled.
Encrypted mail protocols, such as SMTPS on port 465 or SMTP with STARTTLS, protect message contents from being inspected by unauthorized parties. When encryption is not in use, sensitive information such as email headers, message bodies, usernames, and potentially passwords can be exposed to attackers performing packet capture or man-in-the-middle attacks.
Option A is incorrect because port 465 indicates encrypted SMTPS communication, which contradicts the observed plaintext traffic. Option B is incorrect because altered sequence and acknowledgment numbers would indicate session manipulation or injection, not lack of encryption. Option D refers to the function of an SMTP relay but does not describe the observed condition in the traffic.
Cybersecurity operations fundamentals stress the importance of detecting unencrypted protocols during network analysis, as they represent high-risk exposure points. Identifying plaintext email communication is a key responsibility of SOC analysts and often leads to remediation actions such as enforcing TLS or disabling insecure services.
Therefore, the correct conclusion is that mail communication is not encrypted, making Option C the correct answer.