To determine the correct JSON snippet for configuring a new interface according to the YANG model, we need to carefully examine both the YANG model definitions and the provided JSON snippets. Here’s a step-by-step explanation:
YANG Model Analysis:
The ietf-interfaces YANG module defines a container interfaces with a list interface.
Each interface has the following important leaves: name, enabled, and description.
The ietf-ip YANG module augments the interface list with a container ipv4, which includes a list address. Each address has the ip and netmask leaves.
Key Elements in JSON:
To configure an interface, the JSON must include the name of the interface, its enabled status, and the IP address configuration.
The structure should reflect the hierarchy defined by the YANG models.
Options Analysis:
json
Copy code
"ietf-interfaces:interface": {
"name": "Loopback100",
"enabled": true,
"ietf-ip:ipv4": {
"address": [
{
"ip": "10.255.254.1",
"netmask": "255.255.255.0"
}
]
}
}
"ietf-interfaces": {
"interface": {
"name": "Loopback100",
"enabled": true,
"ietf-ip": {
"ipv4": {
"address": [
{
"ip": "10.255.254.1",
"netmask": "255.255.255.0"
}
]
}
}
}
}
"interface": {
"name": "Loopback100",
"enabled": true,
"ipv4": {
"address": [
{
"ip": "10.255.254.1",
"netmask": "255.255.255.0"
}
]
}
}
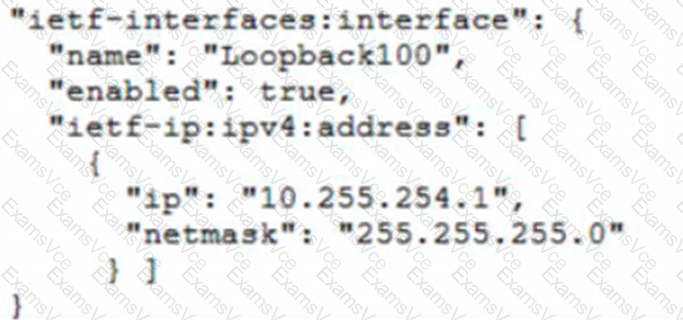
"ietf-interfaces:interface": {
"name": "Loopback100",
"enabled": true,
"ietf-ip:ipv4:address": [
{
"ip": "10.255.254.1",
"netmask": "255.255.255.0"
}
]
}
Correct Explanation:
Option A correctly adheres to the YANG model hierarchy and namespace specifications.
It properly nests address within ipv4, which is itself nested within ietf-ip augmentation to interface.
This structure is consistent with how the YANG models define the relationships between the elements.
References:
Understanding of YANG models and their use: Cisco DevNet YANG Introduction
YANG Data Models in NETCONF: RFC 6020