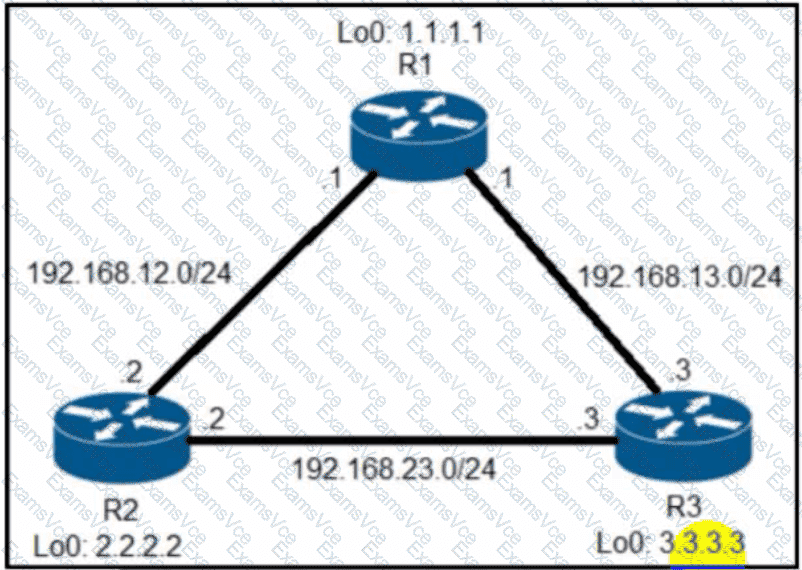
From the output of the “show ip eigrp topology …” command, we notice network 192.168.13.0/24 was learned via two routes:+ From 192.168.23.3 (R3) with FD = 1075200 and AD = 281600+ From 192.168.12.1 (R1) with FD = 2611200 and AD = 281600
From the output of the “show ip route …” command, we learned that the best (and chosen) path is via 192.168.23.3 (R3).
To use both paths (called unequal cost load balancing) with EIGRP, the second path via R1 must satisfy the feasibility condition. The feasibility condition states that, theAdvertised Distance (AD) of a route must be lower than the feasible distance of the current successor route.
In this case, the second path satisfies the feasible condition as its AD (281600) is smaller than the FD (1075200) of the best path. Therefore we can configure loadbalancing with “variance” command.
In other words, EIGRP will install all paths with metric < variance * best_metric into the local routing table, provided that it meets the feasibility condition to preventrouting loop. Therefore we can calculate the variance > metric / best_metric = 2611200 / 1075200 =2.4.
So with a variance greater than 2 (and must be an integer), we can load balance traffic to network 192.168.13.0/24.