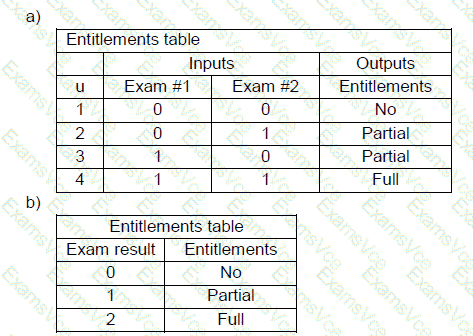
Decision Model and Notation (DMN) is a standardized approach used to model decision logic, often represented in decision tables that evaluate inputs and determine outputs. In this scenario, the entitlements granted to a candidate are based on the total score from two exams, where:
Each exam can be graded as either 0 or 1.
The combined score can be 0, 1, or 2.
The entitlements depend on the combined result:
0 → No entitlements
1 → Partial entitlements
2 → Full entitlements
Among the given diagrams:
Option A simply lists test cases but lacks explicit logic modeling.
Option B shows a mapping from total score to entitlements but doesn't model how the total is derived from the two exams.
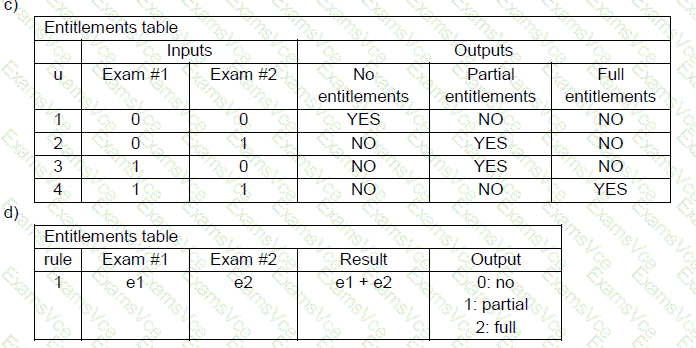
Option C redundantly splits outputs into multiple Boolean fields and doesn't reflect how the decision is made from exam inputs.
Option D is the correct representation.
Option D uses:
e1 and e2 as inputs for Exam #1 and Exam #2.
Result as the sum of e1 + e2.
A final Output mapped based on the Result:
0 → No
1 → Partial
2 → Full
This structure accurately follows the DMN standard by expressing inputs, a derived result, and the corresponding decision output, making Option D the correct and most complete decision model.
Exact Reference – ISTQB CTFL Acceptance Testing Syllabus (Section 2.3):
“Decision tables are commonly used to express business rules that determine outputs based on combinations of inputs. DMN formalizes this structure to support automated reasoning.”