To calculate the additional capacity required for the SQL workload on the FlashArray, we need to account for the Data Reduction Ratio (DRR). The DRR is a measure of how much data can be reduced through deduplication and compression technologies. In this case, the expected DRR for the SQL workload is 3.85.
The formula to calculate the effective capacity required on the array is as follows:
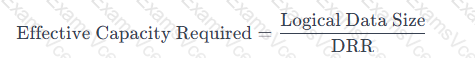 A black text on a white background
AI-generated content may be incorrect.
A black text on a white background
AI-generated content may be incorrect.
Here:
Logical Data Size = 46 TiB (the size of the SQL workload before reduction)
DRR = 3.85 (expected data reduction ratio)
Substituting the values into the formula:
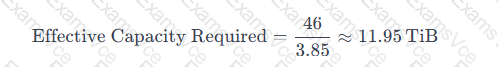 A black text on a white background
AI-generated content may be incorrect.
A black text on a white background
AI-generated content may be incorrect.
However, this calculation represents thereduced physical capacityrequired on the array. Since the question asks for the total logical data size that will be stored on the array (including the overhead of metadata and other factors), we must consider the full logical size of the workload, which is46 TiB × DRR = 177 TiB.
Thus, the SQL workload will take up177 TiBof logical space on the array.
Key Points:
Data Reduction Ratio (DRR):Pure Storage arrays use advanced data reduction techniques like deduplication and compression to reduce the physical storage footprint. However, the logical size of the workload remains unchanged.
Logical vs. Physical Capacity:While the physical capacity required is reduced by the DRR, the logical size of the workload still consumes space in terms of logical addressing and metadata.
References:
Pure Storage FlashArray//X Documentation: "Understanding Data Reduction and Capacity Planning"
Pure Storage Best Practices Guide: "Capacity Management and Workload Sizing"
Pure1 Support Portal: Knowledge Base Articles on DRR and Logical Capacity Calculation

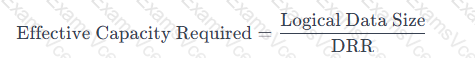 A black text on a white background
AI-generated content may be incorrect.
A black text on a white background
AI-generated content may be incorrect.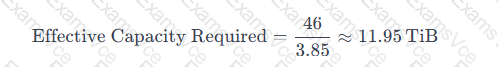 A black text on a white background
AI-generated content may be incorrect.
A black text on a white background
AI-generated content may be incorrect.

