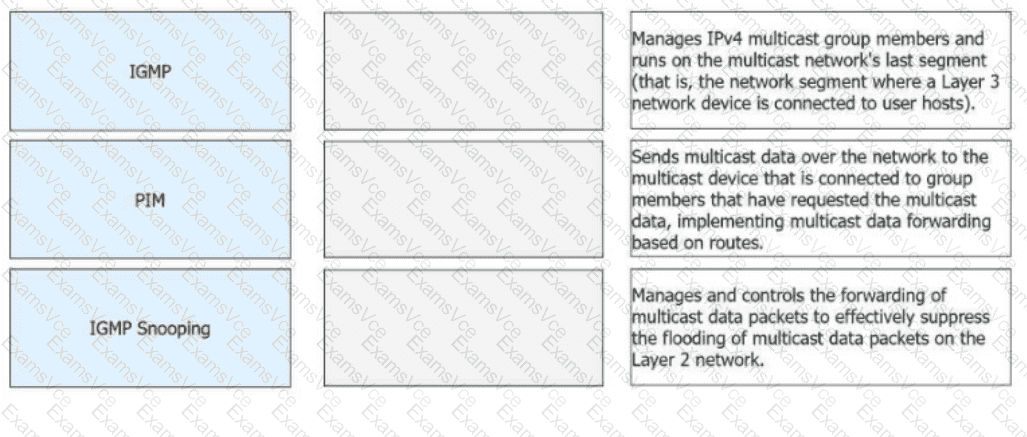
IGMP:Manages IPv4 multicast group members and runs on the multicast network's last segment (that is, the network segment where a Layer 3 network device is connected to user hosts).
PIM:Sends multicast data over the network to the multicast device that is connected to group members that have requested the multicast data, implementing multicast data forwarding based on routes.
IGMP Snooping:Manages and controls the forwarding of multicast data packets to effectively suppress the flooding of multicast data packets on the Layer 2 network.
IGMP (Internet Group Management Protocol):
IGMP is used by hosts and adjacent multicast routers to establish and maintain multicast group memberships on a local subnet.
It allows a host to inform a multicast router of its desire to receive multicast traffic for a specific group.
It operates at Layer 3 and runs on the last segment of the network.
HCIP-Datacom-Core Technology Training Material (Multicast Fundamentals).
PIM (Protocol Independent Multicast):
PIM is a routing protocol designed for efficient routing of IP multicast traffic. It determines the paths over which multicast packets should be forwarded.
PIM is "protocol-independent" because it uses the underlying unicast routing table for RPF (Reverse Path Forwarding) checks.
It is responsible for distributing multicast data throughout the network.
[Reference:HCIP-Datacom-Core Technology Training Material (Multicast Routing Protocols)., IGMP Snooping:, IGMP Snooping operates at Layer 2 and monitors IGMP traffic between hosts and routers., It prevents multicast flooding by allowing a switch to forward multicast packets only to the ports that have joined specific multicast groups., This significantly enhances efficiency in Layer 2 networks with multicast traffic., Reference:HCIP-Datacom-Core Technology Training Material (IGMP Snooping Concepts)., , ]