Comprehensive and Detailed In-Depth Explanation:
1. Understanding MPLS Label Switching
MPLS (Multiprotocol Label Switching) operates by adding labels to packets to enable fast switching across an MPLS domain.
Labels are swapped at each router (LSR - Label Switch Router) based on the LFIB (Label Forwarding Information Base).
When an MPLS packet reaches a router, it checks the incoming label and swaps it with an outgoing label as per its label forwarding table.
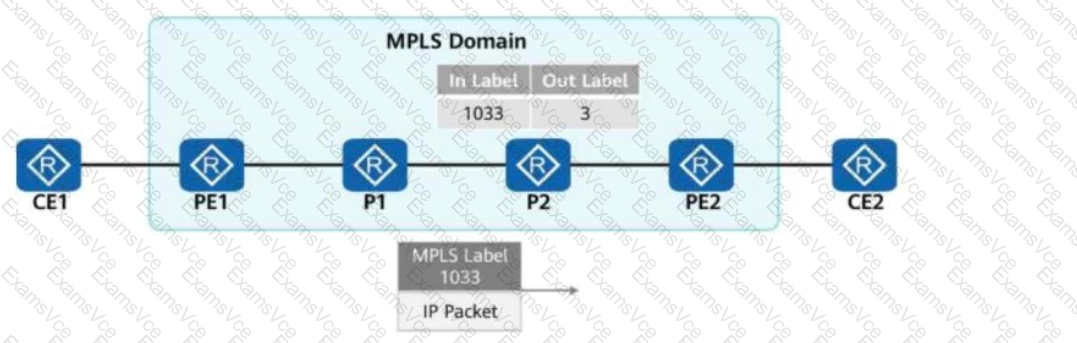
The label value "3" is the implicit null label, which is used for PHP (Penultimate Hop Popping).
2. Analyzing the MPLS Label Flow in the Figure
At PE1: The packet enters the MPLS domain and is labeled with 1033.
At P1: P1 forwards the packet based on label 1033.
At P2:
P2 receives label 1033 and swaps it with label 3 (as per the figure).
Label 3 (implicit null) means that the label is removed before reaching PE2 (PHP - Penultimate Hop Popping).
This ensures that PE2 receives a pure IP packet without an MPLS label.
3. Evaluating Each Answer Option
Option A: "The label value is 3." → Incorrect.
Label 3 (implicit null) is not actually sent to PE2.
Instead, P2 removes the label before sending the packet to PE2.
Option B: "There is no label." → Correct.
Since P2 performs PHP (Penultimate Hop Popping), the label is removed, and PE2 receives only an IP packet.
Option C: "The label value is 1033." → Incorrect.
Option D: "The label values are 3 and 1033." → Incorrect.
Only one label is present at a time.
Label 1033 was swapped for label 3, but label 3 was removed before reaching PE2.
Final Answer:
Answer: B (There is no label).
HCIP-Datacom-Advanced Routing & Switching Technology References:
MPLS Label Forwarding Mechanism
Penultimate Hop Popping (PHP) and Implicit Null Label (3)
MPLS Label Swapping and Label Forwarding Table (LFIB)