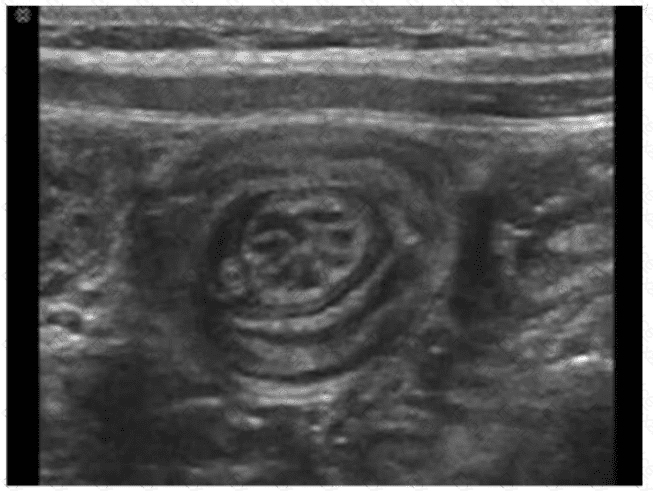
The ultrasound image shows a classic “target sign” or “donut sign,” characterized by concentric rings of alternating echogenicity. This sonographic finding is pathognomonic for intussusception, particularly when seen in the transverse plane.
Intussusception occurs when a segment of bowel telescopes into an adjacent segment, typically in children aged 6 months to 3 years. It commonly presents with intermittent abdominal pain, vomiting, and sometimes “red currant jelly” stools.
Key ultrasound features of intussusception:
Target sign in transverse view (concentric rings of bowel layers)
Pseudokidney or sandwich sign in longitudinal view
May show intraluminal mesenteric fat or vessels dragged in with the intussusceptum
Comparison of answer choices:
A. Bowel obstruction may show dilated loops of bowel with air-fluid levels and to-and-fro peristalsis but lacks the concentric ring sign.
B. Diverticulitis typically shows bowel wall thickening and pericolic fat stranding; not the concentric target appearance.
C. Appendicitis may appear as a blind-ending tubular structure (>6 mm), not with concentric ring pattern.
D. Intussusception — Correct. The image demonstrates the classic target sign seen with this condition.
[References:, Coley BD. US of gastrointestinal tract abnormalities in infants and children. Radiographics. 2005;25(1):27–47., Rumack CM, Wilson SR, Charboneau JW, Levine D. Diagnostic Ultrasound, 5th ed. Elsevier; 2017., AIUM Practice Parameter for the Performance of Pediatric Ultrasound (2021)., , ]