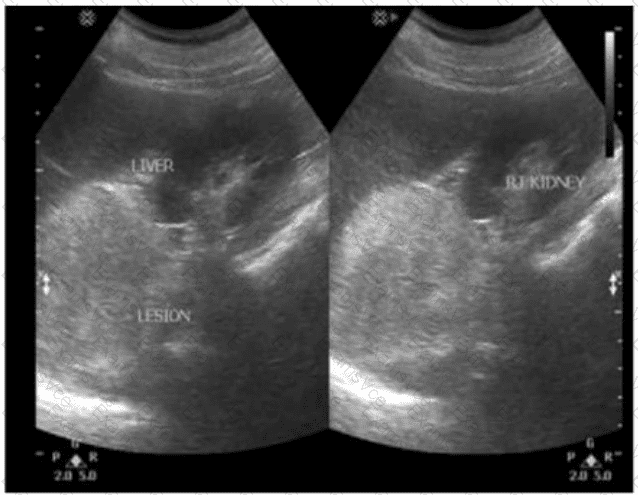
The ultrasound images show a heterogeneous, solid-appearing mass within the right kidney. The patient has a history of hypertension and hematuria—classic clinical features that raise suspicion for renal cell carcinoma (RCC), especially in an adult.
Renal cell carcinoma is the most common primary malignant tumor of the kidney in adults. Common presenting symptoms include:
Hematuria (most frequent symptom)
Flank pain
Palpable abdominal mass
Hypertension (due to increased renin secretion)
Sometimes paraneoplastic syndromes (e.g., polycythemia due to erythropoietin production)
Ultrasound Features of RCC:
Solid renal mass, often with heterogeneous echotexture
May contain cystic components, calcifications, or necrotic areas
May distort the renal contour
Doppler may show internal vascularity
Differentiation from other options:
B. Adenoma: Rare and typically small, benign cortical lesions. They do not typically present with hematuria or hypertension and cannot be reliably distinguished from RCC on ultrasound.
C. Nephroblastoma (Wilms tumor): Pediatric renal tumor seen almost exclusively in children under age 5.
D. Pheochromocytoma: Arises from the adrenal gland (not the kidney); associated with hypertension but not hematuria.
[References:, Rumack CM, Wilson SR, Charboneau JW, Levine D. Diagnostic Ultrasound. 5th Edition. Elsevier, 2018. Chapter: Urinary Tract, pp. 210–222., American College of Radiology (ACR) Appropriateness Criteria – Hematuria, 2022., Radiopaedia.org. Renal cell carcinoma: https://radiopaedia.org/articles/renal-cell-carcinoma, , ]