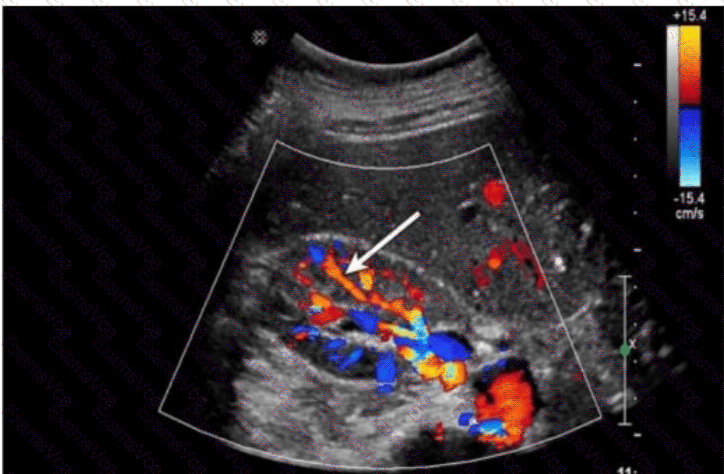
The arrow in this Doppler ultrasound image of the kidney is pointing to vessels located at the corticomedullary junction, arching over the bases of the medullary pyramids. This vascular pattern is characteristic of the arcuate arteries.
Renal arterial anatomy follows a specific branching hierarchy:
Segmental arteries branch off the main renal artery.
Interlobar arteries travel between renal pyramids.
Arcuate arteries arch over the base of the pyramids at the corticomedullary junction.
Interlobular arteries extend into the cortex from the arcuate arteries.
Key characteristics of arcuate arteries on ultrasound:
Located at the corticomedullary junction (between the medullary pyramids and renal cortex).
Run perpendicular to the long axis of the kidney, often forming an arching or curving pattern.
Commonly targeted in Doppler studies to assess resistive index (RI) in renal perfusion studies.
Comparison of answer choices:
A. Interlobular arteries are smaller vessels that extend perpendicularly from the arcuate arteries into the cortex—not visible at this level.
B. Arcuate — Correct. The arrow is indicating these vessels arching over the medullary pyramids.
C. Segmental arteries are larger and deeper, branching off the renal artery near the hilum.
D. Interlobar arteries course between the pyramids but do not arch along their base.
[References:, Rumack CM, Wilson SR, Charboneau JW, Levine D. Diagnostic Ultrasound, 5th ed. Elsevier; 2017., Hagen-Ansert SL. Textbook of Diagnostic Sonography, 8th ed. Elsevier; 2017., AIUM Practice Parameter for the Performance of a Renal Artery Duplex Sonogram (2020)., , ]